PostgreSQL 中的时间戳
最近读到一篇非常好的文章 PostgreSQL 中 timestamp 与 timestamptz 的区别,也可以访问 https://japinli.github.io/2023/03/postgresql-timestamp/,读完这篇文章后学习到了两点
- PostgreSQL 存在两个纪元,Unix 纪元(1970-01-01 00:00:00)和 PostgreSQL 纪元(2000-01-01 00:00:00),在底层存储系统存储的是时间相对于 PostgreSQL 纪元的数值。
EXTRACT(EPOCH FROM source)是基于 Unix 纪元的结果。 - 顺藤摸瓜可以阅读
src/backend/utils/adt/timestamp.c文件中的timestamp_in和timestamp_out函数,从源码上理解时间字符串的输入和输出逻辑。
因此本文的逻辑是基于显示的结果而言,从显示的结果推论可能的原因,只是为了方便理解。推荐阅读它而不是本文。
表示时间戳的数据类型
PostgreSQL 提供了 timestamp 和 timestamptz 两种数据类型来表示时间戳,它们分别是 timestamp without time zone 和 timestamp with time zone 的缩写。timestamp 是标准 SQL 支持的缩写,而 timestamptz 是一种 PostgreSQL 的扩展。从它们的名字就可以知道 timestamp 不包含时区信息,而 timestamptz 包含。
为了学习 PostgreSQL 的时间戳类型我们创建一个测试表 label,每个字段的说明参考下面的建表语句
1 | CREATE TABLE label |
时间戳的输入格式
Valid input for the time stamp types consists of the concatenation of a date and a time, followed by an optional time zone, followed by an optional
ADorBC. (Alternatively,AD/BCcan appear before the time zone, but this is not the preferred ordering.) Thus:1999-01-08 04:05:06and:1999-01-08 04:05:06 -8:00are valid values, which follow the ISO 8601 standard.The SQL standard differentiates
timestamp without time zoneandtimestamp with time zoneliterals by the presence of a “+” or “-” symbol and time zone offset after the time. Hence, according to the standard,TIMESTAMP '2004-10-19 10:23:54'is atimestamp without time zone, whileTIMESTAMP '2004-10-19 10:23:54+02'is atimestamp with time zone. PostgreSQL never examines the content of a literal string before determining its type, and therefore will treat both of the above astimestamp without time zone. To ensure that a literal is treated astimestamp with time zone, give it the correct explicit type:TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE '2004-10-19 10:23:54+02'.In a literal that has been determined to be
timestamp without time zone, PostgreSQL will silently ignore any time zone indication. That is, the resulting value is derived from the date/time fields in the input value, and is not adjusted for time zone.
从这一段描述中我们知道 PostgreSQL 接受 ISO 格式的时间戳,因此我们可以构建下面的插入语句,'2024-05-23 20:17:25' 是我们输入的创建时间,不带时区信息;而 '2024-05-23 20:17:25+08' 是我们输入的更新时间,带有时区信息
1 | test=# INSERT INTO label(name, create_time, update_time) VALUES ('aaa', '2024-05-23 20:17:25', '2024-05-23 20:17:25+08'); |
时间戳的输出格式
The output format of the date/time types can be set to one of the four styles ISO 8601, SQL (Ingres), traditional POSTGRES (Unix date format), or German. The default is the ISO format. (The SQL standard requires the use of the ISO 8601 format. The name of the “SQL” output format is a historical accident.)
ISO 8601 specifies the use of uppercase letter
Tto separate the date and time. PostgreSQL accepts that format on input, but on output it uses a space rather thanT, as shown above. This is for readability and for consistency with RFC 3339 as well as some other database systems.
1 | test=# SELECT * FROM label; |
PostgreSQL 默认输出 ISO 格式。我们发现创建时间和我们输入的时间字符串是一样的,而更新时间和我们输入的时间字符串不一样,一个是小时数少了 8 小时,另一个是时区部分变成了 +00。这是为什么呢?
如何存储时间戳
如何确定当前时区
The built-in default is
GMT, but that is typically overridden inpostgresql.conf; initdb will install a setting there corresponding to its system environment.The TimeZone configuration parameter can be set in the file
postgresql.conf, or in any of the other standard ways described in Chapter 19. There are also some special ways to set it:
- The SQL command
SET TIME ZONEsets the time zone for the session. This is an alternative spelling ofSET TIMEZONE TOwith a more SQL-spec-compatible syntax.- The
PGTZenvironment variable is used by libpq clients to send aSET TIME ZONEcommand to the server upon connection.
在服务器端通过查看 postgresql.conf 文件中 timezone 的值确定当前时区,目前为 Etc/UTC,即 UTC(UTC+0,零时区,下同)
1 | cat /var/lib/postgresql/data/postgresql.conf | grep ^timezone |
在 psql 客户端使用 SHOW TIME ZONE 来查看当前时区,目前与我们服务器设置的时区一致
1 | test=# SHOW TIME ZONE; |
如何修改当前时区
在服务器端通过编辑 postgresql.conf 文件的 timezone 配置来修改时区
1 | sed -i "s/timezone = 'Etc\/UTC'/timezone = 'Asia\/Shanghai'/" /var/lib/postgresql/data/postgresql.conf |
在 psql 客户端使用 SET TIME ZONE 来修改当前时区,这个命令修改的是当前会话的时区,不影响服务器和其他客户端的时区
1 | test=# SET TIME ZONE 'Asia/Shanghai'; |
时间戳的存储尺寸
timestamp 和 timestamptz 的存储尺寸都是 8 个字节,可以通过下面的查询进行验证
1 | test=# SELECT typname, typlen FROM pg_type WHERE typname ~ '^timestamp'; |
8 个字节显然是存不下类似 2024-05-23 20:17:25 这样的时间字符串的,更不要说 2024-05-23 20:17:25+08 这种带时区的更长的字符串了。那么我们可以猜测在内部是使用数值存储时间的,即存储的是距离某个时间的间隔。这个某个时间是多少呢?
我们查看 EXTRACT(field FROM source) 函数在 field 为 EPOCH 时的说明如下
For
timestamp with time zonevalues, the number of seconds since 1970-01-01 00:00:00 UTC (negative for timestamps before that); fordateandtimestampvalues, the nominal number of seconds since 1970-01-01 00:00:00, without regard to timezone or daylight-savings rules; for interval values, the total number of seconds in the interval
1970-01-01 00:00:00 UTC 就是那个某个时间,也被称为纪元时间。
1 | test=# SELECT id, name, create_time, EXTRACT(EPOCH FROM create_time) AS create_time_epoch, update_time, EXTRACT(EPOCH FROM update_time) AS update_time_epoch FROM label; |
总结一下,PostgreSQL 不会保存时区信息,在内部将输入的时间转换为距离 1970-01-01 00:00:00 UTC 的秒数(根据设置的精度 p 可能包含小数)。
存储 timestamptz 时的转换逻辑
For
timestamp with time zone, the internally stored value is always in UTC (Universal Coordinated Time, traditionally known as Greenwich Mean Time, GMT). An input value that has an explicit time zone specified is converted to UTC using the appropriate offset for that time zone.
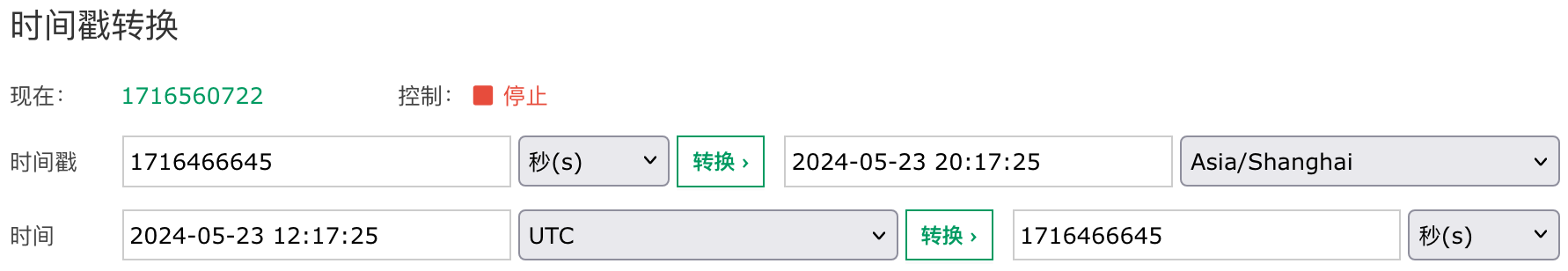
更新时间 '2024-05-23 20:17:25+08' 有明确的时区声明,其中 +08 表示 UTC+8(东八区),它和 UTC 之间相差 8 小时,所以它减去 8 小时为 2024-05-23 12:17:25+00,再把它转换为距离 1970-01-01 00:00:00 UTC 的秒数 1716466645 进行存储。下面是使用工具 https://tool.lu/timestamp 转换的结果
同时我们需要注意,具体应该减去多少时区偏移值只与输入时间中识别到时区有关,与服务器或客户端设置的时区无关,这一点可以参考下面标签 bbb 和 ccc 输入的更新时间的显示结果。
timestamptz 的显示逻辑
When a
timestamp with time zonevalue is output, it is always converted from UTC to the currenttimezonezone, and displayed as local time in that zone. To see the time in another time zone, either changetimezoneor use theAT TIME ZONEconstruct (see Section 9.9.3).
因此,内部存储的更新时间 1716466645 从 UTC 时区转换为当前时区 UTC 进行显示即为 2024-05-23 12:17:25+00。当我们把当前时区修改为 UTC+8 时又会显示为东八区的时间,即我们输入的时间
1 | test=# SET TIME ZONE 'Asia/Shanghai'; |
当我们把当前时区修改为 UTC+9 时又会显示为东九区的时间
1 | test=# SET TIME ZONE 'Asia/Tokyo'; |
同时我们发现无论我们怎么改变时区 EXTRACT 函数的输出始终没有改变,它始终显示的是距离纪元时间的秒数。
存储 timestamp 时的转换逻辑
If no time zone is stated in the input string, then it is assumed to be in the time zone indicated by the system’s TimeZone parameter, and is converted to UTC using the offset for the timezone zone.
创建时间 '2024-05-23 20:17:25' 没有时区,它将按照系统时区与 UTC 之间时区偏移进行转换。当前的系统时区是 Etc/UTC 因此创建时间 '2024-05-23 20:17:25' 被当作 UTC 时区的时间 '2024-05-23 20:17:25+00',然后计算和 1970-01-01 00:00:00 UTC 之间的秒数 1716495445 进行存储。
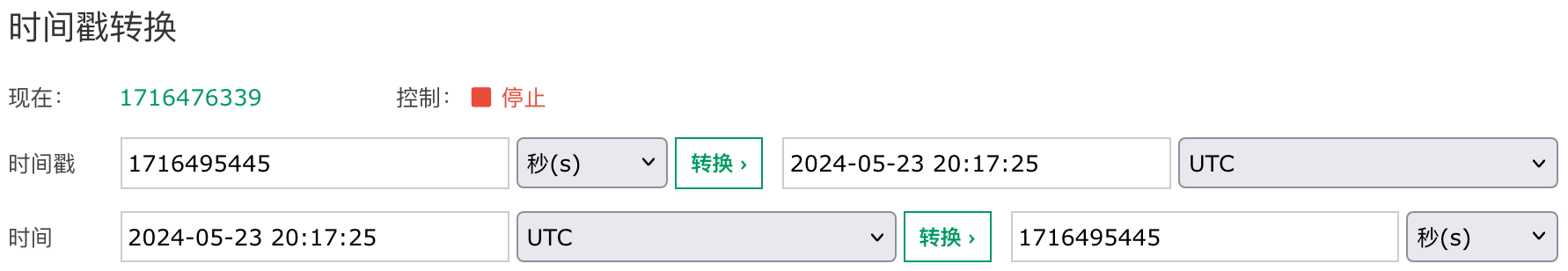
这是完全按照上面描述的逻辑进行的转换,因为当前的时区就是 Etc/UTC,所以结果看起来没什么问题。我们来尝试一个不同的时区,把服务器的时区需改为 UTC+9(东九区)后再来看看这个转换逻辑是否正确。因为我们当前在 UTC+8(东八区)时区,为了避免我们自己所在的时区对转换逻辑的干扰,所以选择设置为 UTC+9 时区。
1 | sed -i "s/timezone = 'Etc\/UTC'/timezone = 'Asia\/Tokyo'/" /var/lib/postgresql/data/postgresql.conf |
重启服务器后再写入一条标签名称为 bbb 的记录,写入记录的语句除了标签名称不一样其他都一样
1 | test=# SHOW TIME ZONE; |
按照上面描述的逻辑我们来进行转换,目前当前时区是 Asia/Tokyo,'2024-05-23 20:17:25' 被当作 UCT+9 时区的时间 '2024-05-23 20:17:25+09',然后计算和 1970-01-01 00:00:00 UTC 之间的秒数 1716463045 进行存储。
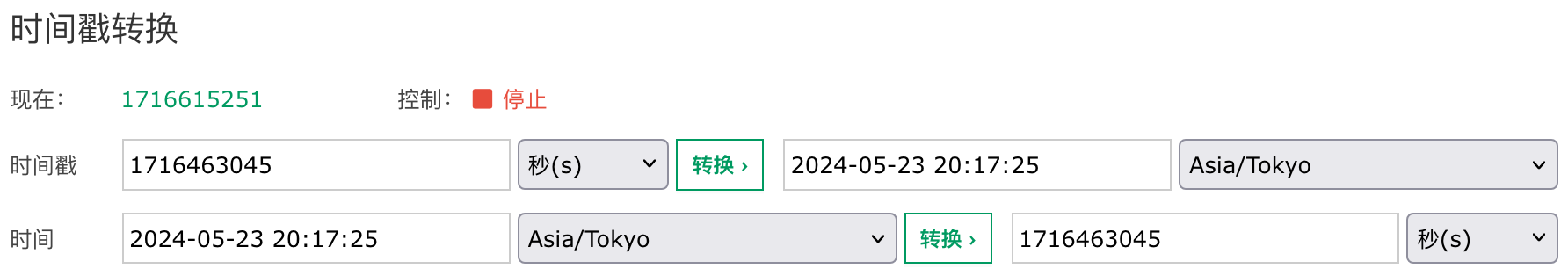
然而这与我们实际查询出来的数据不一样,标签 bbb 的创建时间(在 UTC+9 时区时写入)与标签 aaa 的创建时间(在 UTC+0 时区时写入)是一样的
1 | test=# SELECT id, name, create_time, EXTRACT(EPOCH FROM create_time) AS create_time_epoch, update_time, EXTRACT(EPOCH FROM update_time) AS update_time_epoch FROM label; |
到底哪里出了问题呢?通过分析发现我们受到了 then it is assumed to be in the time zone indicated by the system’s TimeZone parameter 这句话的误导。实际上,对于 timestamp without time zone 类型 PostgreSQL 不会进行时区转换,它把输入的时间当作 UTC 时间,然后计算和 1970-01-01 00:00:00 UTC 之间的秒数并存储这个秒数。即使输入的时间带有时区信息,比如 '2024-05-23 20:17:25+02',PostgreSQL 也会忽略掉任何时区信息,只使用输入值的日期和时间部分进行计算
1 | test=# INSERT INTO label(name, create_time, update_time) VALUES ('ccc', '2024-05-23 20:17:25+02', '2024-05-23 20:17:25+08'); |
只有把输入的时间忽略掉任何时区信息并把它当作 UTC 时间才能保证当修改服务器或者客户端的时区时,存储在 timestamp without time zone 类型里的时间才不会改变,才能保证在任何时区下显示的值就是输入的值。